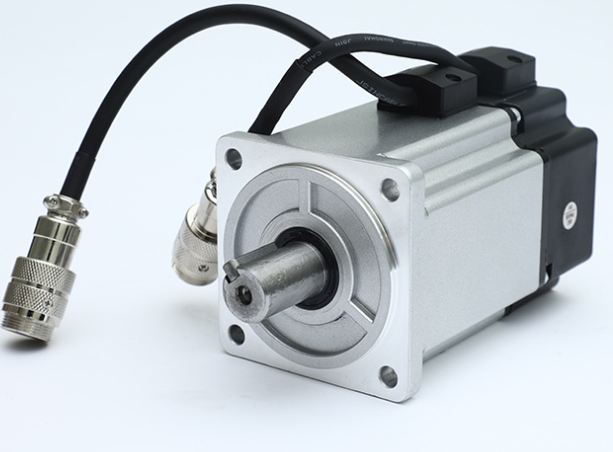
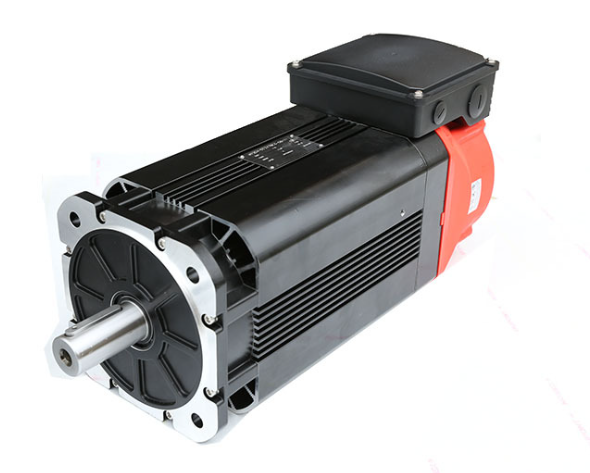
Industrial robot servo control VS step control VS frequency conversion control. The peripheral motion control part of industrial robots mainly has three parts: servo control, step control, and frequency conversion control, let’s answer these control points one by one.
Industrial robot servo control VS step control VS frequency conversion control
First, the working principle of AC servo motor
The rotor inside the servo motor is a permanent magnet, the drive controls the U/V/W three-phase electricity to form an electromagnetic field, the rotor rotates under the action of this magnetic field, and the encoder feedback signal of the motor comes with the driver, and the drive compares with the target value according to the feedback value and adjusts the angle of rotor rotation. The accuracy of the servo motor depends on the accuracy (number of lines) of the encoder.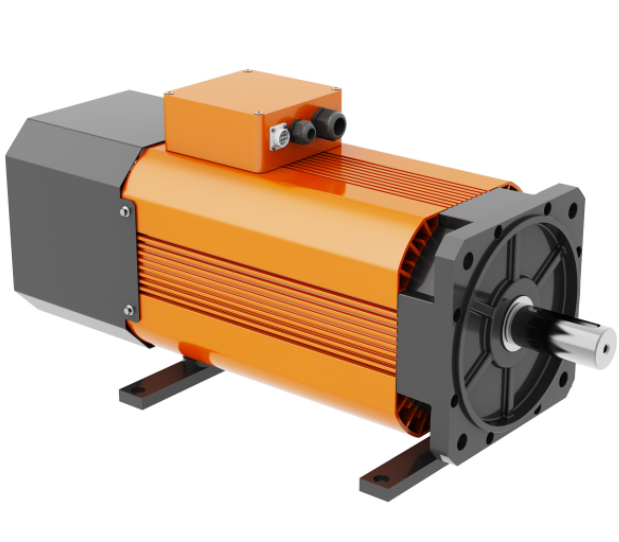
Second, the composition and classification composition of the servo system
Servo system is a general term for control systems with position and angle as the control quantity, and the system with the speed, angular velocity, acceleration, force, etc. associated with position and angle as the control quantity is also included in the servo system.
classify
1. According to the classification of control structure, it is divided into: open-loop type and closed-loop type.
2. According to the classification of drive components, it is divided into:
a. Stepper motor servo system.
b. DC motor servo system.
c. AC motor servo system.
Third, the characteristics of servo motor (AC).
1. High positioning accuracy, ordinary servo motor can reach 0.036 degrees
2. Fast response time.
3. The control is convenient and flexible, and the control system is easy to implement.
4. There are many models, and different types can be selected according to different application environments.
5. Provide full closed-loop control, which can monitor the operation status in a timely manner and make appropriate adjustments and transformations.
Fourth, the servo system structure
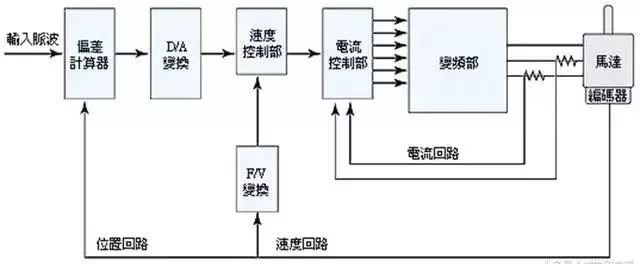
Fifth, Selection steps of servo control
1. Determine mechanical specifications, load, rigidity and other parameters.
2. Confirm the action parameters, movement speed, stroke, acceleration and deceleration time, cycle, accuracy, etc.
3. Select motor inertia, load inertia, motor shaft conversion inertia, rotor inertia.
4. Select the motor rotation speed.
5. Select the rated torque of the motor. Load torque, acceleration and deceleration torque, instantaneous maximum torque, actual torque.
6. Select the resolution of the mechanical position of the motor.
7. Select the motor model according to the above.
Application of step control
First, the working principle of the stepper motor
A stepper motor is an actuator that converts electrical impulses into angular displacement. When the stepper driver receives a pulse signal, it drives the stepper motor to rotate a fixed angle (called “step angle”) in the set direction, and its rotation is run step by step at a fixed angle. The amount of angular displacement can be controlled by controlling the number of pulses, so as to achieve the purpose of accurate positioning; At the same time, the speed and acceleration of motor rotation can be controlled by controlling the pulse frequency, so as to achieve the purpose of speed regulation. Stepper motor can be used as a special motor for control, and it is widely used in various open-loop control by taking advantage of its characteristics of no accumulated error (accuracy of 100%).
Second, the classification of stepper motors
Stepper motors commonly used now include reactive stepper motors (VR), permanent magnet stepper motors (PM), hybrid stepper motors (HB) and single-phase stepper motors.
●Permanent magnet stepping motor is generally two-phase, torque and volume are small, and the stepping angle is generally 7.5 degrees or 15 degrees;
●Reactive stepper motor is generally three-phase, which can achieve large torque output, and the step angle is generally 1.5 degrees, but the noise and vibration are large. The rotor magnetic routing of the reactive stepper motor is made of soft magnetic material, and there are multi-phase excitation windings on the stator, which uses the change of magnetic conductance to generate torque.
●Hybrid stepper motor refers to the advantages of mixing permanent magnet type and reactive type. It is divided into two-phase and five-phase: the two-phase step angle is generally 1.8 degrees, while the five-phase stepping angle is generally 0.72 degrees. This stepper motor is the most widely used.
Third, stepper motor system
1. Static index terminology for stepper motors
a. Number of phases: the number of pairs of excitation coils that generate different polarity N and S magnetic fields. Commonly used m denotation. b. Number of beats: the number of pulses or conductive state required to complete a periodic change of a magnetic field is expressed in n, or refers to the number of pulses required for the motor to turn a pitch angle.
c. Step angle: corresponding to a pulse signal, the angular displacement of the motor rotor is represented by θ.
d. Positioning torque: the locking torque of the motor rotor itself (caused by the harmonics and mechanical errors of the magnetic field tooth shape) when the motor is not energized.
e. Static torque: the locking torque of the motor shaft when the motor does not rotate under the action of rated static electricity.
2. Dynamic indicators and terminology of stepper motors
a. Step angle accuracy: the error between the actual value and the theoretical value of each step angle of the stepper motor.
b. Out of step: The number of steps run when the motor is running, not equal to the theoretical number of steps. Call it a steplessness.
c. Offset angle: The angle at which the rotor tooth axis is offset from the stator tooth axis.
d. Maximum no-load starting frequency: the maximum frequency at which the motor can be started directly without load under a certain drive form, voltage and rated current.
e. Maximum no-load operating frequency: the highest speed frequency of the motor without load under a certain drive form, voltage and rated current.
f. Operating torque-frequency characteristics: The curve of the relationship between output torque and frequency measured by the motor under certain test conditions is called the operating torque-frequency characteristics.
Fourth, stepper motor selection
1. Selection of step angle: The step angle of the motor depends on the requirements of load accuracy.
2. Selection of static torque: The selection of static torque is based on the load of the motor work, under normal circumstances, the static torque should be 2-3 times the friction load.
3. Current selection: Due to different current parameters, its operating characteristics vary greatly, and the current of the motor can be judged according to the torque-frequency characteristic curve
Fifth, some characteristics of stepper motor
1. Generally, the accuracy of the stepper motor is 3-5% of the stepping angle, and it is not cumulative.
2. The maximum allowable temperature of the stepper motor is generally above 130 degrees Celsius.
3. The torque of the stepper motor will decrease with the increase of speed.
4. The stepper motor can operate normally at low speed, but if it is higher than a certain speed, it cannot be started, accompanied by a whistling sound.
5. Stepper motor is used in low-speed occasions— the speed does not exceed 1000 revolutions per minute.
Sixth, Comparison of the performance of the two motors
1. The control accuracy is different
The step angle of five-phase hybrid stepper motor is generally 0.72 °, 0.36 ° AC servo motor control accuracy is guaranteed by the rotary encoder at the back end of the motor shaft, for the motor with standard 2500 line encoder, its pulse equivalent is 360 ° / 10000 = 0.036 °, servo motor accuracy is higher than stepper motor.
2. Low frequency characteristics are different
Stepper motors are prone to low-frequency vibration at low speeds. The AC servo motor runs very smoothly and does not vibrate even at low speeds.
3. The overload capacity is different
Stepper motors generally do not have overload capacity. AC servo motor has strong overload capacity.
4. Different running performance
The control of the stepper motor is open-loop control, the starting frequency is too high or the load is too large is easy to lose steps or stall the phenomenon, the speed is too high when stopping, the phenomenon of overshoot, the AC servo drive system is closed-loop control, the drive can directly sample the motor encoder feedback signal, the internal composition of the position loop and the speed loop, generally there will be no stepper motor step loss or overshoot phenomenon, the control performance is more reliable.
5. Different speed response performance
It takes 200~400 milliseconds for stepper motor to accelerate from standstill to working speed (generally hundreds of revolutions per minute). The acceleration performance of the AC servo system is better, taking Panasonic MSMA 400W AC servo motor as an example, it only takes a few milliseconds to accelerate from static to its rated speed of 3000RPM, which can be used in control occasions that require fast start and stop.
6. The torque-frequency characteristics are different
The output torque of the stepper motor decreases with the increase of speed, and it will drop sharply at higher speeds, and the AC servo motor is a constant torque output.
In summary, AC servo systems are superior to stepper motors in many performance aspects. However, in some occasions with low requirements, stepper motors are often used as executive motors. Therefore, in the design process of the control system, it is necessary to comprehensively consider the control requirements, cost and other factors, and select the appropriate control motor.
Frequency conversion control
First, the introduction of general motors
Three-phase squirrel cage AC motor is one of the most common induction motors, and its structure and characteristics are as follows:
Schematic diagram of the structure of an induction motor
Schematic diagram of the structure of the motor
Characteristics of the motor
Second, the principle and composition of the frequency converter
The frequency converter is a control device that can change the speed of the AC motor simply and freely. The method to change the speed of the AC motor is as follows.
The frequency converter realizes speed regulation by changing the AC motor power frequency:
The composition of the frequency converter is as follows:
1. Converter (rectifier)
A large number of diode bridge rectifiers are used, as shown in Figure 1, which convert a power frequency supply to a DC supply. It is also possible to form a reversible converter with two sets of transistor converters, which can be regenerated due to its reversible power direction.
2. Flat wave circuit
In the rectified DC voltage of the rectifier, there is a pulsation voltage of 6 times the frequency of the power supply, and the pulsating current generated by the inverter also causes the DC voltage to fluctuate. To suppress voltage fluctuations, inductors and capacitors are used to absorb pulsating voltages (currents). The device capacity is small, and if there is a margin between the power supply and the main circuit component device, the inductor can be omitted and a simple flat wave loop can be used.
3. Inverter
In contrast to the rectifier, the inverter converts the DC power into AC power at the required frequency, and turns the 6 switching devices on and off at a determined time to obtain a 3-phase AC output.
4. Brake circuit
When an asynchronous motor is used in the regenerative braking area (the slip rate is negative), the regenerative energy is stored in the flat wave loop capacitor, which increases the DC voltage. Generally speaking, the energy accumulated by the inertia of the mechanical system (including the motor) is larger than the energy stored by the capacitor, and when rapid braking is required, the regenerative power can be dissipated by using a reversible converter to feedback to the power supply or setting the brake circuit (switch and resistor) to avoid the voltage of the DC circuit from rising.
Third, the application purpose and use of the frequency converter
The adjustable speed transmission composed of frequency converter and AC motor is called frequency converter drive, and its functional use is as follows. They may be related to each other, in fact there is no clear classification, and this table is for reference only.



