Step angle calculation of stepper motor, what is the formula?
Step angle θ = 360 degrees / (number of rotor teeth × number of running beats).
The step angle of the motor indicates the angle at which the motor rotates for each pulse signal sent by the control system. In other words, the angle at which the rotor turns for each input pulse electrical signal is called the distance angle and is expressed by θ.
Step angle calculation of stepper motor, what is the formula? CNC stepper motor
Take conventional two- and four-phase motors with 50-tooth rotor teeth as an example. The step angle is θ=360 degrees / (50×4) = 1.8 degrees (commonly known as the whole step) when four beats are running, and the step angle is θ = 360 degrees / (50×8) = 0.9 degrees (commonly known as half step) when eight beats are running.
Stepper motors have a fixed resolution, such as a stepper motor with a resolution of 24 steps per revolution, and the step angle is 15°.
The advantages of using small step angles to complete a certain incremental movement in several steps are: small overshoot during operation, inconspicuous oscillation, and high precision. The accuracy and speed requirements of the system should be weighed when choosing.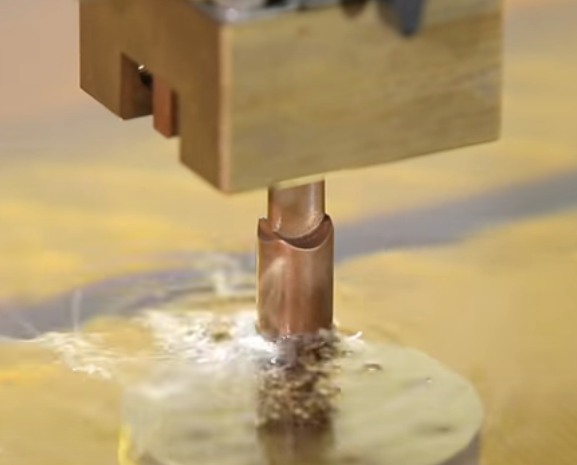
Stepper motors are used in EDM machines – CNC EDM Machine
Common ones are 3°/1.5°, 1.5°/0.75°, 3.6°/1.8°.
For example, for a stepper motor (small motor) with a step angle of 1.8 degrees, the number of pulses used for one revolution is n=360/1.8=200 pulses.
The error of the step angle will not accumulate for a long time, only corresponding to the number of input pulse signals, and can form an open-loop control system with a relatively simple structure and certain accuracy, or a closed-loop system when higher accuracy is required.
The determination of step angle can directly use precision goniometering equipment such as reading microscopes and photoelectric encoders to measure the angle of each pulse. Since the stepper motor receives a pulse signal, it must turn a certain angle accordingly.
In the inspection test, the method of presetting the number of pulses Nf can also be used to check the number of steps per revolution, and indirectly check whether the step angle is correct.
How to calculate the step angle of a stepper motor?
The step angle of a stepper motor refers to the angle at which each motor is rotated in one step.
To calculate the step angle of a stepper motor, you need to know the number of steps of the motor and the rotation angle of the motor.
42 series stepping motor – NEMA 17 stepper motor with double shaft
For example, if a 4-phase 2A motor requires 400 steps per revolution, the step angle of the stepper motor is:
Step angle = 360 degrees / Number of steps = 360 degrees / 400 = 0.9 degrees
Therefore, the step angle of this stepper motor is 0.9 degrees.
Step angle calculation of stepper motor:
Motor intrinsic step angle:
It represents the angle at which the motor rotates for each step pulse signal sent by the control system.
The motor gives a step angle value when leaving the factory, such as SL86S2114A motor gives a value of 0.9 ° / 1.8° (indicating 0.9 ° when working in half a step, 1.8° when working in a full step), this step angle can be called ‘inherent step angle of the motor’, it is not necessarily the real step angle when the motor actually works, the real step angle is related to the drive.
The number of phases of the motor is different, and the step angle is also different.
Generally, the step angle of two-phase motors is 0.9°/1.8°, the three-phase is 0.75°/1.5°, and the five-phase is 0.36°/0.72°.
In the absence of subdivision drives, users mainly rely on choosing stepper motors with different phase numbers to meet their step angle requirements.
1.8 degree stepper motor meaning
If a subdivision drive is used, the ‘phase number’ becomes meaningless, and the user can change the step angle simply by changing the number of subdivisions on the drive.
Taking a four-phase motor as an example, there are four-phase four-beat operation mode, namely AB-BC-CD-DA-AB, the four-phase eight-beat operation mode is A-AB-B-BC-C-CD-D-DA-A, the rotor tooth is a 50-tooth motor as an example, the step angle is θ=360 degrees / (50*4)=1.8 degrees when running in four beats, and the step angle is θ=360 degrees / (50*8)=0.9 degrees when running eight-beats.
Stepper motors have a basic step angle. The two-phase is 1.8°. The three-phase is 1.2°.
If you want to know the step angle after subdivision. Just use 360 degrees / number of pulses required per revolution = step angle per step.
Q=360/MZK
This is the step angle calculation formula of the stepper motor running in the three-phase six-beat drive mode.









