Is the difference between a three-phase stepper motor and a two-phase stepper motor only 2 and 3?
In the industrial field, we will often use stepper motors and are familiar with them, but who knows where the difference between motors with different phases is, today I will share it with you.
Stepper motors are first classified according to the number of phases, and generally we have four phases, two phases, and three phases.
Therefore, the small editor of this article first introduces where is the distance between the three-phase stepper motor and the two-phase stepper motor, the first introduction is the difference between them, and then discusses the distance between the three-phase stepper motor and the two-phase stepper motor step angle, and specifically follows the Xiaobian to understand it specifically.
130mm 3-Phase Stepper Motor
The difference between a three-phase stepper motor and a two-phase stepper motor
1. The number of phases of the motor
It means that the number of coils inside the motor is different, the two-phase stepper motor motor is composed of 2 coils inside, and the three-phase stepper motor is composed of 3 coils inside.
 5A 37N.M three-phase stepper motor
5A 37N.M three-phase stepper motor
2. The step angle of the motor
It refers to the viewpoint of each step of the motor, generally the step angle of two-phase motors on the market is 0.9°/1.8°, and the three-phase is 0.75°/1.5°.
3. The scale of the motor
Three-phase motors are generally large motors, so the scale will generally be larger than two-phase motors, which also determines that three-phase stepper motors work more smoothly than two-phases.
4. Torque
The torque of a two-phase motor will be slightly larger than that of a three-phase motor with the same scale.
5. Accuracy
The subdivision function of the two-phase stepper motor driver is becoming more and more robust, and the two-phase can also reach the accuracy that the three-phase can reach.
130mm 3-Phase Stepper Motor – Nema 52 3-phase motor for stage lighting machinery and equipment automation control
The high-speed performance of the three-phase stepper motor is good (the characteristics are harder), and the step angle is smaller and the accuracy is better than that of the two-phase stepper motor.
Because torque decreases slowly with increasing speed, it is generally used in applications where high precision is required.
Analyze and interpret the gap between three-phase stepper motors and two-phase stepper motors
Detailed explanation of the step angle of three-phase stepper motor and two-phase stepper motor

130mm Three-phase stepper motor
1. Elements that determine the step angle
The higher the stepper motor resolution (the number of steps in a revolution, 360° divided by the step angle), the higher the azimuth accuracy. In order to obtain high resolution, the number of poles should be planned. PM type rotor is N and S poles placed at equal pitch on the outer surface of the core of the rotor, and the number of rotor poles is the sum of N poles and S poles, in order to simplify the explanation, the number of pole pairs is assumed to be 1. Here, the step angle θs of the stepper motor that determines that the rotor is a permanent magnet is indicated by the following equation, where Nr is the number of rotor pole pairs and P is the number of stator phases, (the HB type stepper motor Nr described later in this lesson is the number of rotor teeth):
The physical meaning of the above equation is as follows:
The mechanical viewpoint of one rotation of the rotor is 360.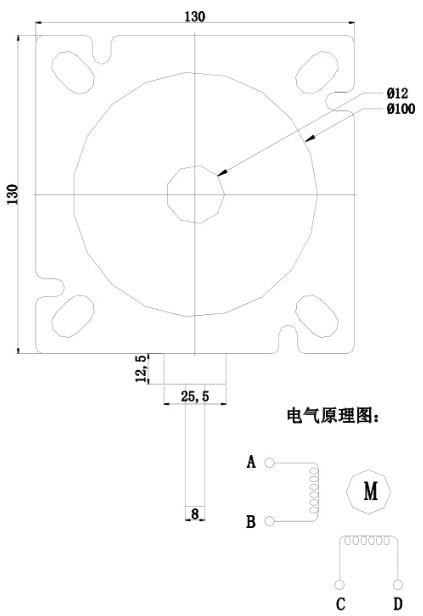
130mm nema 52 stepper motor dimensions
If the number of poles is used to remove 2Nr, it is equivalent to the mechanical viewpoint occupied by one pole, that is, 180°/Nr. That is to say, the mechanical viewpoint of a pole is cut with the number of stator phases to obtain the step angle, and this concept is shown in the figure below.
It can be seen from the formula θs=180°/PNr that the smaller the step angle, the higher the resolution, so to improve the resolution of the stepper motor, it is necessary to add the number of rotor pole pairs or choose a multiphase method with more stator phase number P. The addition of Nr is limited by machining, so to make a high-resolution stepper motor, two methods are required.
Dimensional drawing of NEMA 52 stepper motor
2. Two-phase stepper motor
The simplest composition of a two-phase stepper motor is the condition of Nr=1, and the motor structure is shown in the figure below. Generally, the number of stator poles of a two-phase motor is a multiple of 4, at least 4. The rotor is a two-pole rotor with an N pole and an S pole.
The stator is generally made of silicon steel sheet stacking, and the number of magnetic poles of the stator is 4 poles, which is equivalent to one phase winding occupying two poles, the two poles of phase A differ by 180° in space, and the two poles of phase B also differ by 180° in space. The current moves positively and negatively in the one-phase winding (this driving method is called bipolar drive), the phase difference between the A phase and the B phase current is 90°, and the rectangular wave current in the two-phase winding replaces the flow.
That is, the stator of the two-phase motor, when Nr = 1, the space difference is 90°, the current is 90° phase difference at all times, the current is similar to the general synchronous motor, a rotating magnetic field occurs on the stator, and the rotor is attracted by the rotating magnetic field and rotates synchronously with the rotating magnetic field.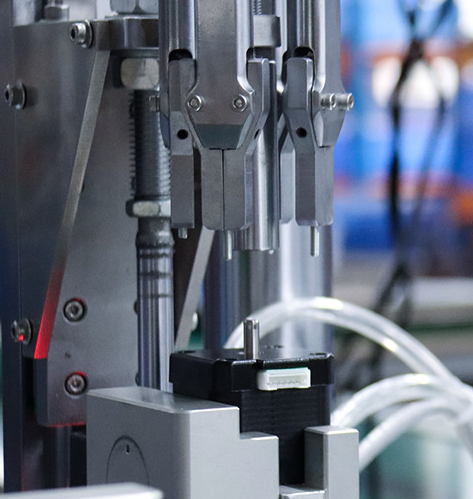
Applications for NEMA 52 stepper motors – Is the difference between a three-phase stepper motor and a two-phase stepper motor only 2 and 3?
The above figure shows the structure of the two-phase stepper motor (PM type) and its working principle, from figure (a) to figure (b) rotated clockwise by 90°, sequential diagram (c), (d) both rotated 90°, sequential continuous work became successive rotation.
As an example in the figure above, assuming that phase A has two coils, unidirectional current can also replace the flow through the two coils, and the opposite direction of magnetic flux can also occur, this method is called unipolar (uni-plar) type coil.
As shown in the figure below, only one-way current flows inside the coil, which is called a unipolar coil; On the other hand, the coil that flows through the forward and reverse currents in the coil is called a bipolar coil, and the advantages and disadvantages of the two coils will be introduced in the following lessons. The unipolar coil can replace the bipolar coil shown in the figure above and operate with the same step angle.
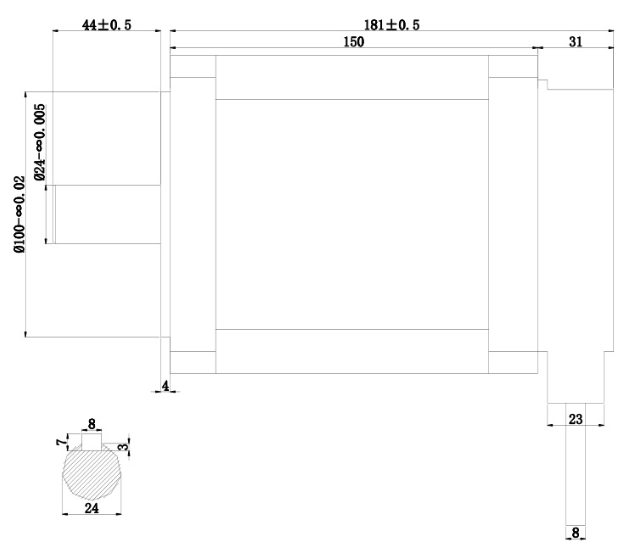 nema 52 stepper motor dimensions
nema 52 stepper motor dimensions
This article analyzes where the distance between the three-phase stepper motor and the two-phase stepper motor is
The two-phase unipolar coil in the figure above is also called a four-phase stepper motor in some literature, and at this moment, the number of rotor pole pairs, the number of teeth Nr, and the step angle θs are the same as the bipolar coil.
The boundary theory of the two-phase motor in this course conforms to the formula θs=180°/PNr, that is, the number of rotor teeth and step angle θs substitute θs=180°/PNr, if P=2, it is a two-phase motor, if Nr is the same, P=4, the step angle θs is only 1/2, then the motor is a four-phase motor, special attention is paid to this.
Two-phase stepper motor is now widely used, the structure ratio of the practice motor (PM bipolar two-phase stepper motor structure and working principle) is messy, the stator in addition to the selection of lamination, there is also a claw pole structure, but the basic principle can refer to the figure (PM bipolar two-phase stepper motor structure and working principle), the rotor shown in the figure is called PM type (permanent magnet or permanent magnet) rotor, the outer surface of the magnetic cylinder forms the rotor pole.
 dv 3722 drive manual pdf
dv 3722 drive manual pdf
3. Three-phase stepper motor
Stepper motors (VR type or reactive or variable reluctance type) that do not use permanent magnets for rotors have long been used in three-phase stepper motors. In 1986, the Japanese servo company developed a stepper motor with a rotor as a permanent magnet and stator poles with teeth (the planning principle of the pole teeth will be introduced later), and the coordination of the tooth pitch of the stator and rotor can obtain higher angular resolution and torque. The number of main poles of the stator coil of a three-phase stepper motor is a multiple of three, so the number of stator main poles of a three-phase stepper motor is 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.

Nema 52 3-phase motor for stage lighting machinery and equipment automation control
Stepper motors (VR type or reactive or variable reluctance type) that do not use permanent magnets for rotors have long been used in three-phase stepper motors. In 1986, the Japanese servo company developed a stepper motor with a rotor as a permanent magnet and stator poles with teeth (the planning principle of the pole teeth will be introduced later), and the coordination of the tooth pitch of the stator and rotor can obtain higher angular resolution and torque. The number of main poles of the stator coil of a three-phase stepper motor is a multiple of three, so the number of stator main poles of a three-phase stepper motor is 3, 6, 9, 12, etc.
The figure below shows the comparison of the typical stator structure and drive circuit of stepper motors with different phase numbers, in which the rotor structure diagram is neglected.
It is assumed that the rotors are all PM type or HB type, and the corresponding rotors are equipped according to the stator for two-phase, three-phase, and five-level equipment.
 NEMA 52 Three-Phase Stepper Motor – Three-phase motor for automated control of mechanical equipment
NEMA 52 Three-Phase Stepper Motor – Three-phase motor for automated control of mechanical equipment
The stator chooses the minimum principal pole number structure that does not occur unbalanced electromagnetic force (it will be introduced later, the sum of the radial attraction of the rotor cannot completely cancel each other out, and the remaining radial force occurs), that is, when the two phases are 4 main poles, the three phases are 3 main poles, and the five phases are 5 main poles, the unbalanced electromagnetic force will occur in the structure, and the above structure will not be used except for special uses.
Nema 52 stepper motor
In the figure, the structure of the stator is the simplest structure with 8 main poles in two phases, 6 main poles in three phases, and 10 main poles in five phases.
On the other hand, such as the bipolar type (Bi-polar) coil used in the stepper motor drive circuit, the number of power tubes, two phases is 8, five phases are 10, three-phase because of the winding selection of Y or △ connection method, 3 outlet drive only 6 power tubes are enough, so from the motor and drive as a whole, the three-phase stepper motor structure is the simplest, and the production cost of the two is the lowest.
NEMA 52 stepper motors product
From the odd and even number of stator phases, the number of switching power tubes in the drive circuit under odd conditions is less than in even cases, for example, the number of drive power tubes in a three-phase stepper motor is less than that of a two-phase stepper motor.
Three-phase driver ICs are now available from manufacturers such as Sanquan Electric Corporation, Sanyo Electric Corporation, and Shindengen Industrial Corporation.
nema 52 3 phase stepper motor
Compared with the two-phase stepper motor, the three-phase stepper motor has the advantages of 1.5 times the resolution and oscillation lower when the number of rotor teeth is the same, so the number of applications will be added, the price will decrease, and it is expected that it can become a serial stepper motor, and its performance will be introduced later.









